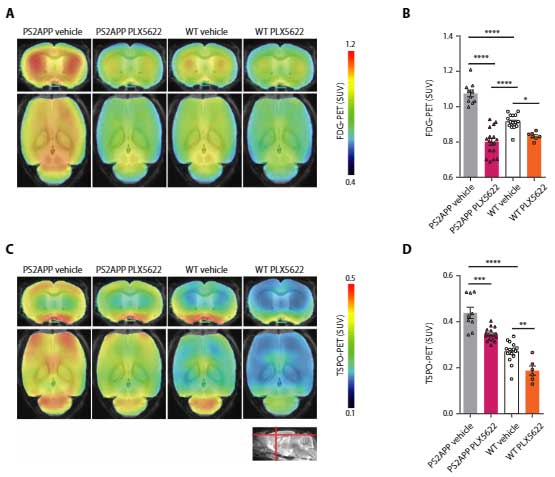
アルツハイマー病(Alzheimer's disease, AD)のバイオマーカーとして、
血漿中のAβ/タウ/NfLの組み合わせの報告(こちら)、
血漿中のp-tau181の報告(こちら)等、
色々でてきていますが、
今回は脳脊髄液(cerebrospinal fluid, CSF)中のp-tau217が、Aβ PET陽性となる前から上がっていて、CSF中p-tau181よりも特異度が高い、というお話。
p-tau217とp-tau181の比較
From ワシントン大学/Gui de Chauliac病院/Montpellier大学
一つ目は、アメリカ・ワシントン大学のBarthelémyら、フランス・Gui de Chauliac病院のGabbelleら、Montpellier大学のLehmannらの研究グループから 。
Background Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker profiles characterized by decreased amyloid-beta peptide levels and increased total and phosphorylated tau levels at threonine 181 (pT181) are currently used to discriminate between Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. However, these changes are not entirely specific to Alzheimer’s disease, and it is noteworthy that other phosphorylated isoforms of tau, possibly more specific for the disease process, have been described in the brain parenchyma of patients. The precise detection of these isoforms in biological fluids remains however a challenge. Methods In the present study, we used the latest quantitative mass spectrometry approach, which achieves a sensitive detection in cerebrospinal fluid biomarker of two phosphorylated tau isoforms, pT181 and pT217, and first analyzed a cohort of probable Alzheimer’s disease patients and patients with other neurological disorders, including tauopathies, and a set of cognitively normal controls. We then checked the validity of our results on a second cohort comprising cognitively normal individuals and patients with mild cognitive impairments and AD stratified in terms of their amyloid status based on PiB-PET imaging methods. Results In the first cohort, pT217 but not pT181 differentiated between Alzheimer’s disease patients and those with other neurodegenerative diseases and control subjects much more specificity and sensitivity than pT181. T217 phosphorylation was increased by 6.0-fold in patients with Alzheimer’s disease whereas T181 phosphorylation was only increased by 1.3-fold, when compared with control subjects. These results were confirmed in the case of a second cohort, in which the pT217 cerebrospinal fluid levels marked out amyloid-positive patients with a sensitivity and a specificity of more than 90% (AUC 0.961; CI 0.874 to 0.995). The pT217 concentrations were also highly correlated with the PiB-PET values (correlation coefficient 0.72; P
もっと特異度の高いマーカーを探すため、Montpellier Memory Research and Resources Centerに登録されたAD患者のCSFを調べた。
また、2ndコホートとして、認知機能正常、軽度認知機能障害(mild cognitive impairment, MCI)、AD患者のPiB-PETデータと比較した。
- Montpellierコホート:AD, n = 10; non-AD, n = 40 (FTLD n = 9, LBD n = 9, PSP n= = , ACIH, n = 6, mixed dementia n = 2, 癌脳転移 n = 1, 認知機能正常n = 5)
- WUSTLコホート:Amyloid(-), n = 51; Amyloid(+), n = 33
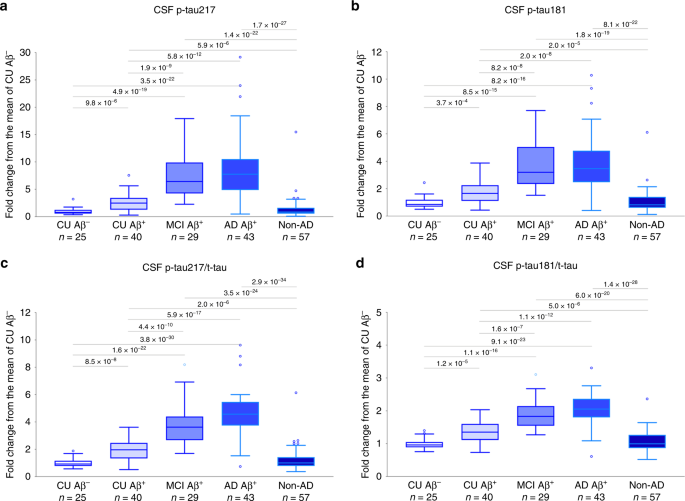
結果、pT217はpT181よりも、ADと他のタウオパチーとを識別できた。
pT217はAD患者で6倍上昇しており、pT181は1.3倍だった。
CSF中pT217量の多い患者は、Amyloid PETでも陽性を示し、特異度は90% (AUC 0.961; CI 0.874 to 0.995)、相関率は0.72(p <0.001)だった。
From Lund大学/Janssen Research & Development/イーライリリー
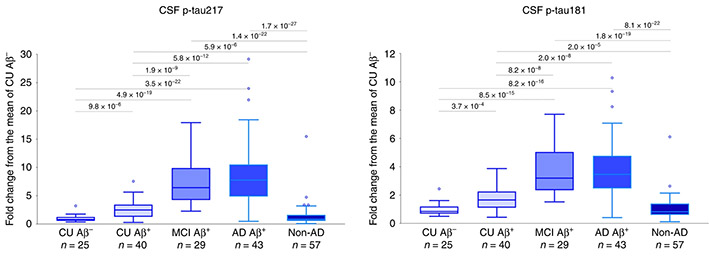
もう一つは、スウェーデン・Lund大学のHansson、Hanelidzeら、アメリカ・Janssen Research & DevelopmentのKolb、イーライリリーのDageらの研究グループから 。
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) p-tau181 (tau phosphorylated at threonine 181) is an established biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) reflecting abnormal tau metabolism in the AD brain. Here the authors demonstrate that CSF p-tau217 shows better performance as an AD biomarker than p-tau181.
CSF中のp-tau217がp-tau181よりも優れたバイオマーカーとなり得るかどうか、調べた。
Swedish BioFINDERコホート(n = 194)では、p-tau217はタウPET([18F]flortaucipir)によるタウ蓄積量と強い相関を示し、経時的に増える様子も確認できた。
p-tau217はp-tau181に比べてCSF中AβやアミロイドPETでのAβ蓄積量との相関が強く、ADとAD以外の認知症をよりよく識別できた。
もう一つのコホート(EXPEDITION3、n = 32)でも同様の結果を得た。
これらの結果は、p-tau217はp-tau181よりも優れたバイオマーカーとなり得る事を示唆している。
My View
今回は、CSFでのバイオマーカーとして、p-tau217の方がp-tau181よりも感度・特異度が高く、ADとそれ以外のタウオパチーとの識別に有望との事。
p-tau181は血漿中でも測定可能(Janelidze et al., Nat Med, 2020; Thijssen et al., Nat Med, 2020)という事なので、需要は高いと思いますが、そのうち血漿中p-tau217の報告も出てくるのでしょう。
以前、凝集タウの構造の違いを認識して、ADやそれ以外のタウオパチーを識別する抗体を作ろうと色々考えていましたが、リン酸化の場所で識別できるのであれば、そして特異度が高いのであれば、そっちの方が簡単でいいかも、と思いました。
バイオマーカー、どんどん出てくるな……
References
- Barthélemy, N.R., Bateman, R.J., Hirtz, C. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid phospho-tau T217 outperforms T181 as a biomarker for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and PET amyloid-positive patient identification. Alz Res Therapy 12, 26 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-020-00596-4
- Janelidze, S., Stomrud, E., Smith, R. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun 11, 1683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15436-0
- Janelidze, S., Mattsson, N., Palmqvist, S. et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat Med 26, 379–386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0755-1
- Thijssen, E.H., La Joie, R., Wolf, A. et al. Diagnostic value of plasma phosphorylated tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat Med 26, 387–397 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0762-2