パーキンソン病 (Parkinson's disease, PD) などのシヌクレイノパチーでは、α-シヌクレイン (α-Syn) の異常凝集、蓄積が起こる。
α-Synモノマーは脂質に作用してシナプス小胞のトラフィッキングに関与するとも考えられている。
α-Synオリゴマーは、細胞膜やミトコンドリア膜の脂質酸化、ミトコンドリアタンパクの酸化etc.を介して、ミトコンドリアのアポトーシスを誘導する事が知られている。
しかしながら、最近、鉄→脂質酸化を介したフェロトーシスによる細胞死が存在する事も報告された(Conrad et al., Genes Dev, 2018)。
今回、イギリス・UCL研究所のAbramov, Gandhiらの研究グループは、α-Synがフェロトーシスによる細胞死を誘導する事を明らかにした。
Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: an interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidationProtein aggregation and abnormal lipid homeostasis are both implicated in neurodegeneration through unknown mechanisms. Here we demonstrate that aggregate-membrane interaction is critical to induce a form of cell death called ferroptosis. Importantly, the aggregate-membrane interaction that drives ferroptosis depends both on the conformational structure of the aggregate, as well as the oxidation state of the lipid membrane. We generated human stem cell-derived models of synucleinopathy, characterized by the intracellular formation of α-synuclein aggregates that bind to membranes. In human iPSC-derived neurons with SNCA triplication, physiological concentrations of glutamate and dopamine induce abnormal calcium signaling owing to the incorporation of excess α-synuclein oligomers into membranes, leading to altered membrane conductance and abnormal calcium influx. α-synuclein oligomers further induce lipid peroxidation. Targeted inhibition of lipid peroxidation prevents the aggregate-membrane interaction, abolishes aberrant calcium fluxes, and restores physiological calcium signaling. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation, and reduction of iron-dependent accumulation of free radicals, further prevents oligomer-induced toxicity in human neurons. In summary, we report that peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids underlies the incorporation of β-sheet-rich aggregates into the membranes, and that additionally induces neuronal death. This suggests a role for ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease, and highlights a new mechanism by which lipid peroxidation causes cell death.
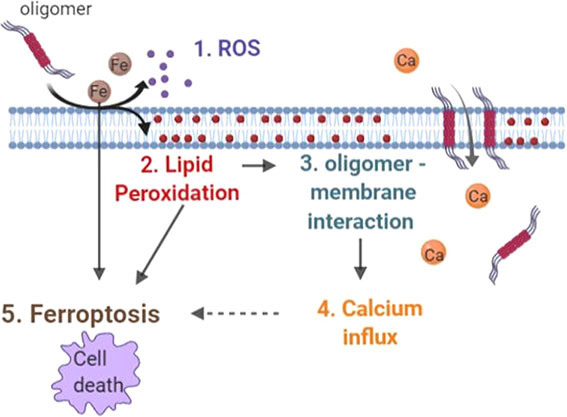
α-Synオリゴマーがフェロトーシスを誘導する
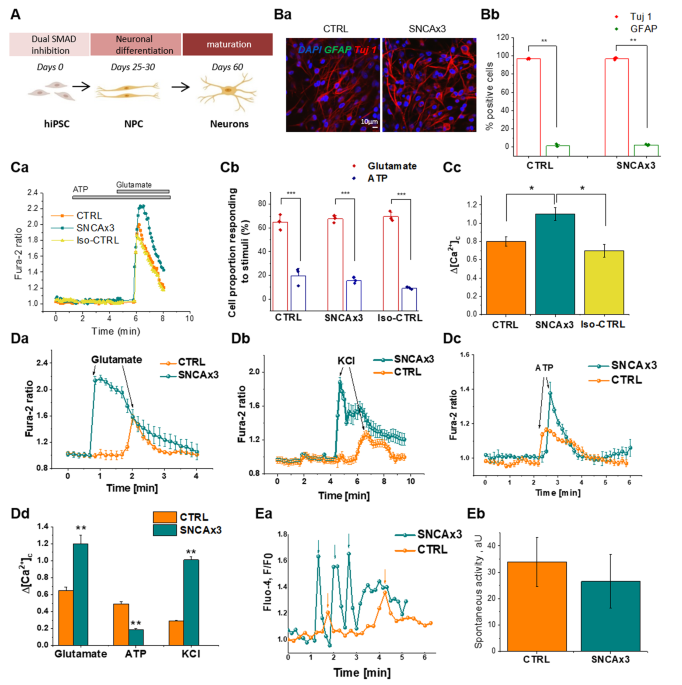
彼らは、SNCAトリプリケーションの患者(SNCAx3)と健常人の皮膚からiPS細胞を樹立し、神経細胞に分化させた。
これら細胞にα-Synのアプタマーを処置すると、SNCAx3細胞では、健常人細胞と比較してα-Synオリゴマーの量が多かった。
また、細胞膜の障害があり、カルシウム流入量も多くなっていた。
さらに、酸化ストレスや脂質酸化も上がっていた。
SNCAx3細胞は、細胞の生存率が経時的に減少したが、
金属イオンのキレーター(Dexferoxamine, DFO)や脂質酸化抑制剤(D4-Lnn)、フェロトーシス阻害剤(Ferrostatin-1)などで処置すると、細胞死が抑制された。
以上の結果から、α-Synオリゴマーは、
(1) 酸化ストレス
(2) 細胞膜の脂質酸化
(3) オリゴマーx細胞膜の相互作用
(4) カルシウム流入↑
(5) フェロトーシス
という流れで細胞死を誘導している可能性が示唆された。
My View
ちょっと前にアルツハイマー病(AD)とフェロトーシスの話を紹介しましたが(こちら)、今回はシヌクレイノパチーとの関与についてのお話。
PDでは黒質緻密部のドパミン神経細胞の脱落がみられ、より鉄代謝との関連が示唆されると思うので、フェロトーシスによる細胞死もしっくりきます。
ただ、著者らはSNCAトリプリケーション由来iPS→神経細胞で
(1) α-Synオリゴマーが増えている事
(2) 細胞内Ca2+流入が増えている事
(3) この現象がα-SynのP129抗体でブロックされる事
でオリゴマー→細胞障害としていますが、
モノマーやフィブリルもたぶん増えていると思うし、α-SynP129抗体ブロックされると思うので、α-Synのどのフォームが最も関与するかはまだ決定できないように思います。
まだまだ色々調べられそうですね。
References
- Angelova, P.R., Choi, M.L., Berezhnov, A.V. et al. Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: an interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidation. Cell Death Differ (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0542-z
- Conrad M, Kagan VE, Bayir H, et al. Regulation of lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in diverse species. Genes Dev. 2018;32(9-10):602‐619. doi: 10.1101/gad.314674.118