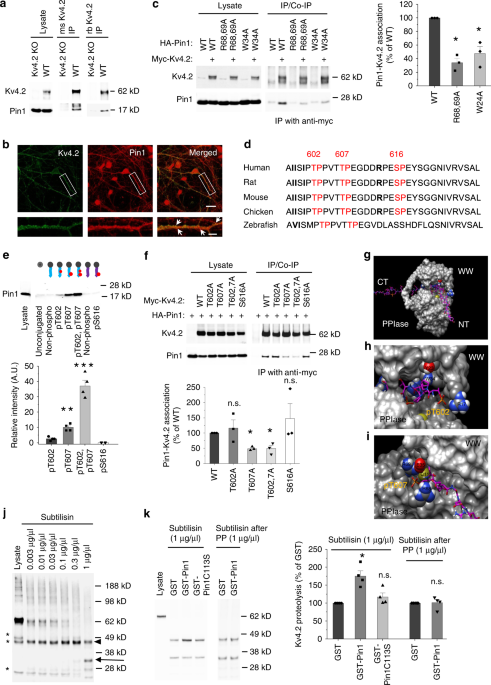
K+チャネル機能は脳機能を調節する。
National Institute of Child Health and Human DevelopmentのHoffmanらのグループは、peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (Pin1) が、A型K+チャネルサブユニット Kv4.2 とその補助サブユニット dipeptidyl peptidase 6 (DPP6) を調節し、認知の柔軟性を調整する事を突き止めた。
K + channels function in macromolecular complexes with accessory subunits to regulate neuronal function. Here, the authors describe Pin1-mediated regulation of the Kv4.2 complex, which impacts reversal learning in mice, providing potential treatment for disorders characterized by cognitive inflexibility.
認知の柔軟性を上げる遺伝子変異
神経活動によりKv4.2 がリン酸化 → Pin1が結合してKv4.2とDPP6複合体が形成される。
著者らは、KCND2 (Potassium Voltage-Gated Channel Subfamily D Member 2) の、Pin1結合サイトを変異(T607A)させたノックインマウス(Kv4.2TA)を作製した。
Kv4.2TAマウスは海馬のCA1錐体細胞でKv4.2-DPP6の複合体形成が変化し、A型K+流量が上がり、神経活動が下がった。
また、行動解析では、Morris水迷路試験とレバー押し試験で、逆転学習能力が向上した。
これらの結果は、Pin1介在メカニズムが逆転学習を司る事を示唆し、認知の柔軟性障害をきたす精神神経疾患の治療ターゲットとして期待される。
References
- Hu, J., Malloy, C., Tabor, G.T. et al. Activity-dependent isomerization of Kv4.2 by Pin1 regulates cognitive flexibility. Nat Commun 11, 1567 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15390-x
NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH (NIH)
- ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 27 March 2020.<www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/03/200327141518.htm>